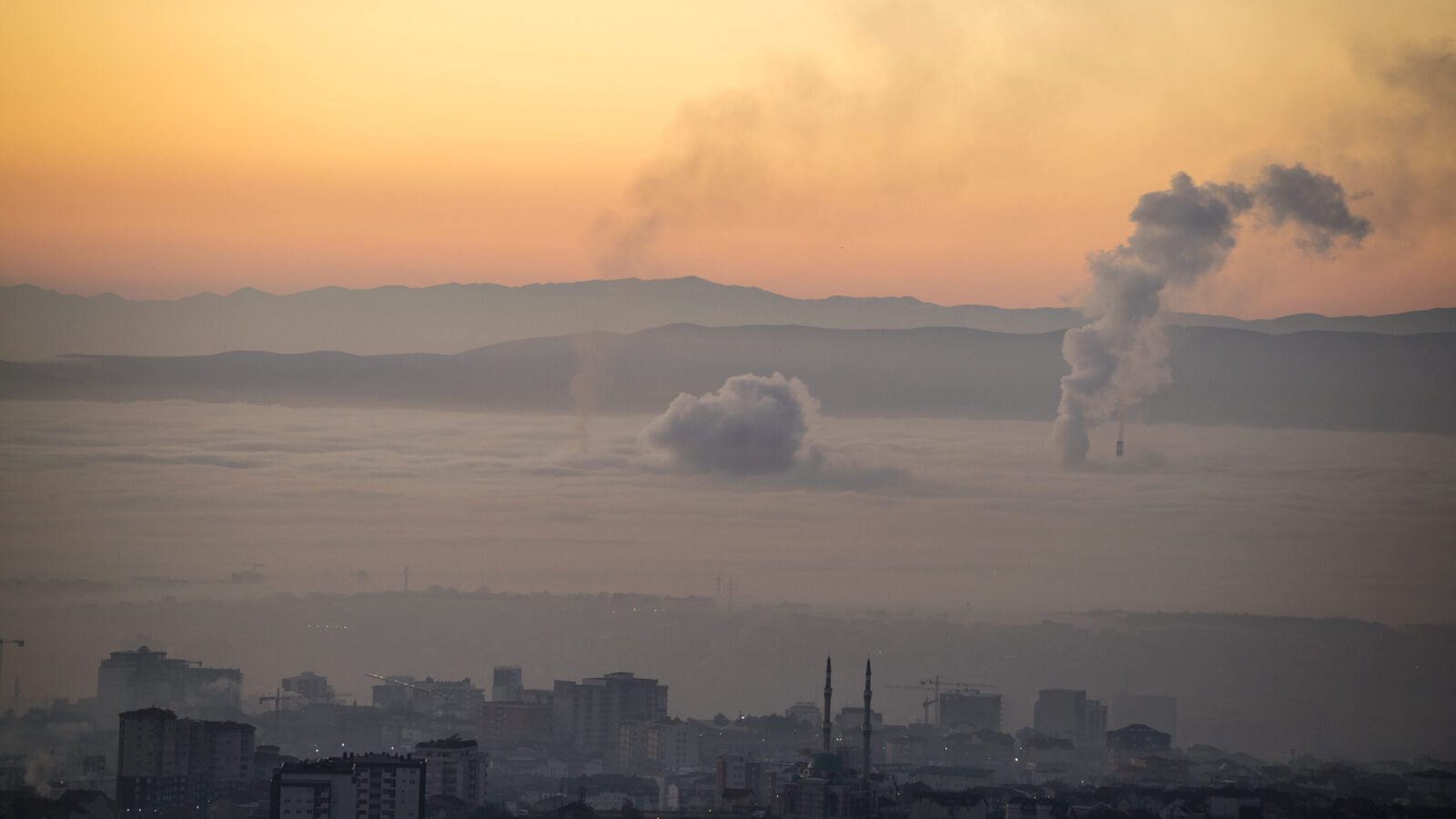
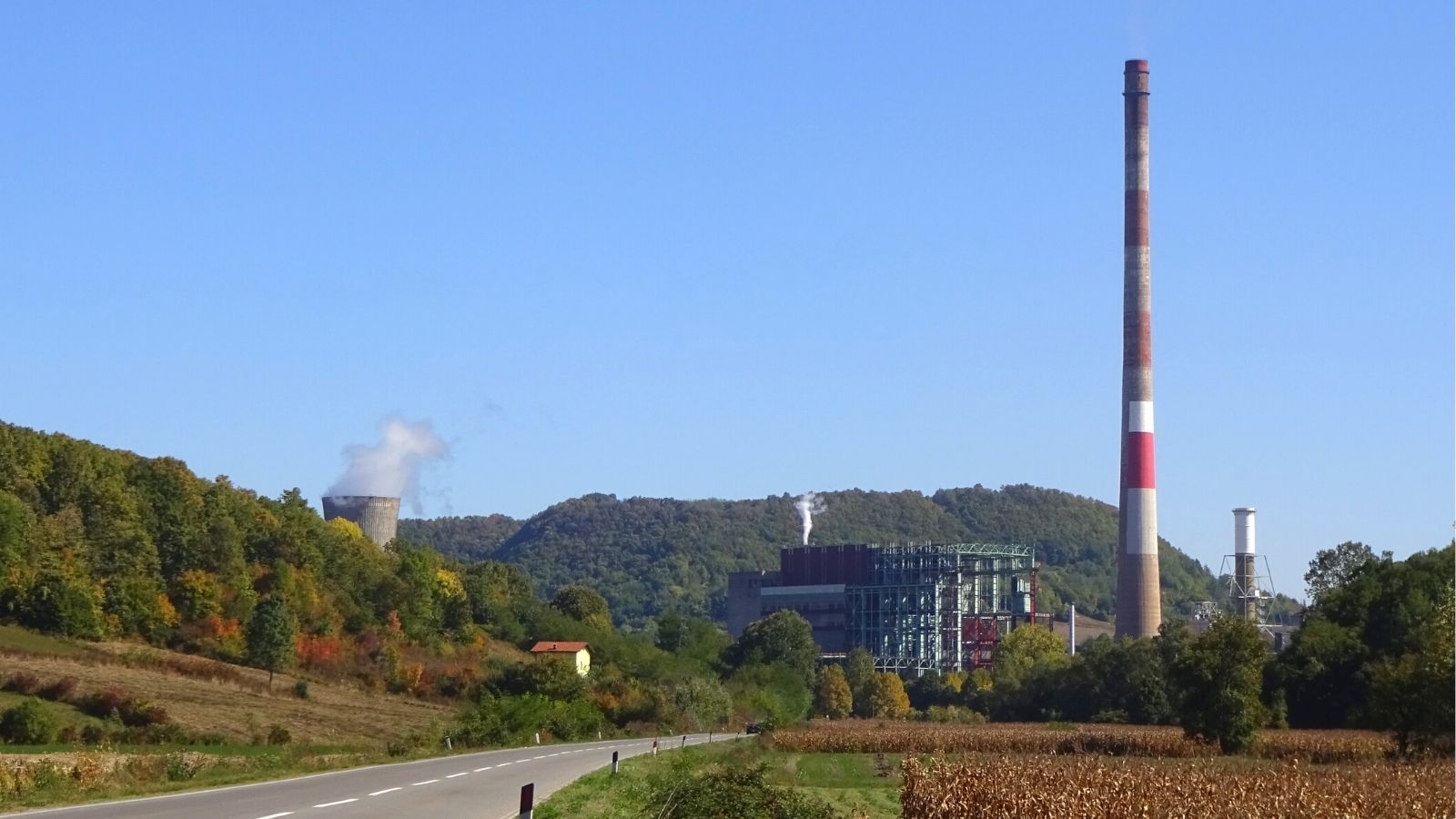
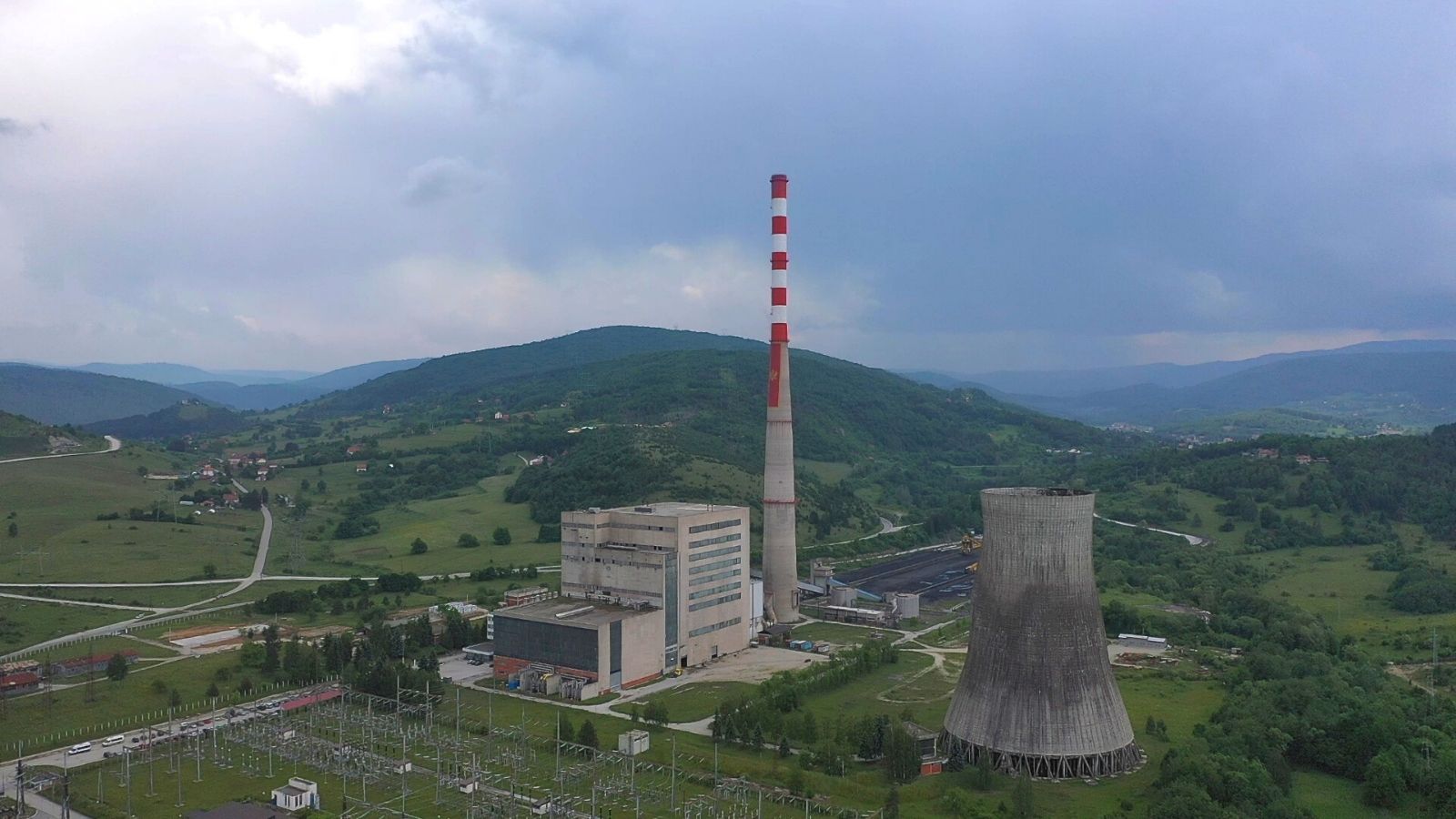
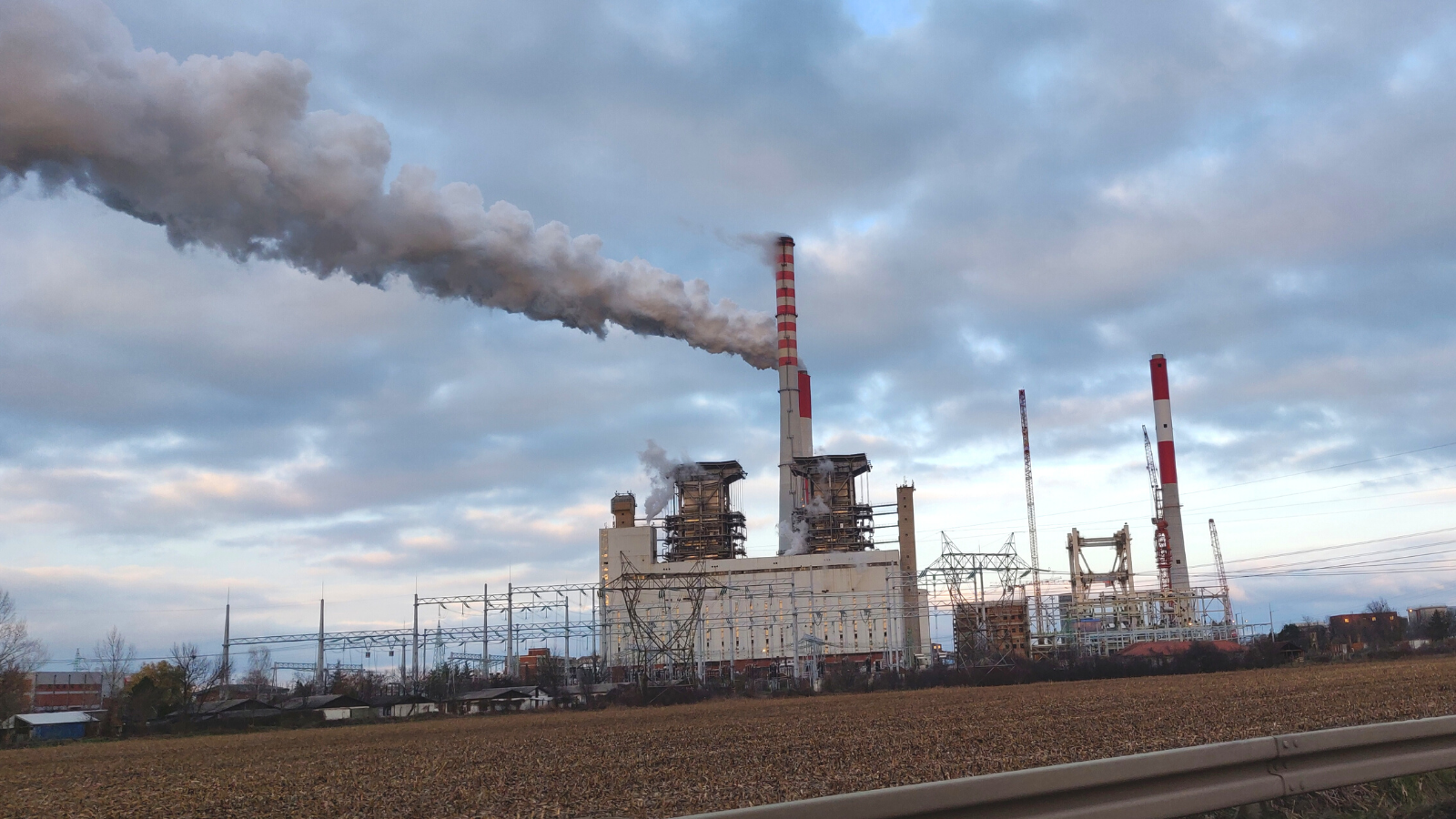
Fossil fuels are fast losing their social license. It is becoming increasingly evident that countries’ continued reliance on dirty hydrocarbons escalates the climate crisis, worsens air pollution and enables war.
Long touted as a ‘bridge fuel,’ fossil gas now needs to be recognised by policymakers for the hurdle to the energy transition that it is, and multilateral development banks should urgently end support for gas projects and gas-dependent companies.
The energy transition has to be just and fast, with citizens, municipalities and workers as critical participants in the process. We are working to ensure no more public money is spent on coal, and public finance is used to accelerate this transition.
Stay informed
We provide updates in English from the Balkans and other coal regions.
IN FOCUS
Fossil gas
Fossil gas is the new coal. Although often labelled ‘natural,’ fossil gas is a major driver of the climate crisis. There is no more room for new investments in fossil gas projects if we are to avert the worst impacts of the climate crisis and set a path towards decarbonisation.

District heating
District heating and individual heating are still dominated by fossil fuels and inefficient burning of wood without regard to sustainability criteria, in combination with a low degree of energy efficiency. This has to change, since heating plays a crucial role in the transition into a clean and zero-carbon economy.
Just transition
No one should be left behind when we reconstruct our world into one driven by clean energy. Working on just transition brings all actors who believe in fair regional redevelopment to the same table: unions, industry, public administration, governments, civil society and others sharing this goal.

Documentary: Turning the Tide
Our documentary exposes, for the first time, the extent of financial support four of the world’s leading multilateral development banks (MDBs) – the World Bank, the European Investment Bank, the Asian Development Bank and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development – have been providing to the global fossil fuels industry over the past 13 years.
Our analysis shows that since 2008, the oil, coal and gas business has been enjoying no less than EUR 81.5 billion in support from these government-owned financial institutions in the form of loans, grants, credit lines and guarantees.
Coal projects
Ugljevik power plant, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Commissioned in 1985, the 300 MW coal power plant in Ugljevik, Bosnia and Herzegovina, has become famous for emitting more sulphur dioxide than all of Germany’s coal power plants in 2019.
Pljevlja I power plant, Montenegro
The existing 225 MW Pljevlja thermal power plant in the north of Montenegro, near the borders with Serbia and Bosnia-Herzegovina, has been operating since 1982. The plant was originally planned to comprise two units but the second one was never built. The plant, along with the extensive use of coal and wood for heating, has caused unbearably bad air quality in the town.
Kostolac B power plant (B1, B2), Serbia
The Kostolac B power plant, consisting of 2 units of 350 MW each, first entered into operation in 1987. In 2022, the plant delivered 4388 GWh of electricity to the grid, nearly 20 per cent of the country’s coal-based generation.
Latest news
Hooked on gas: CEE governments’ climate plans prescribe fossil gas addiction
Blog entry | 16 July, 2024During much of the past 13 months – the longest streak of record-breaking global temperatures – EU governments have been revising their climate strategies. Yet, instead of increasing ambition at a time of a climate emergency, as they have committed to do, policymakers in central and eastern Europe appear keen to sustain their countries’ addiction to fossil gas.
Read moreUrgent call for central and eastern European countries to raise their NECP climate ambitions
Press release | 27 June, 2024With the deadline (30 June) for EU Member States to submit their national energy and climate plans (NECPs) fast approaching, concerns are growing that CEE countries are not showing the ambition needed to meet their 2030 climate and energy targets.
Read moreEU climate fund bankrolling dirty energy expansion
Press release | 25 June, 2024As global temperatures continue to soar and climate disasters hit the most vulnerable, the EU’s little-known Modernisation Fund is propping up unsustainable energy infrastructure.
Read moreRelated publications
Request for information on EIB role in Ostroleka C coal-fired power plant in Poland
Advocacy letter | 3 October, 2011 | Download PDFPress information from September 2011 suggested that ENERGA S.A. is holding conversations with the European Investment Bank about financing a new coal-fired unit in Rzekun also referred to as Ostroleka C. With this letter, Bankwatch inquired whether the EIB is having conversations with ENERGA S.A. and if yes, at which stage they are.
The Polnoc power plant in Poland. A plan for the biggest greenfield coal project in Europe.
Briefing | 10 August, 2011 | Download PDFAt a whopping 2000 MW, the planned Polnoc power plant (Elektrownia Polnoc) in northern Poland would be the largest greenfield coal-fired power plant in Europe. Located in the Pomerania region, which until now has had no coal industry and in recent years has witnessed an unprecedented surge in the wind energy projects, the plant would sit perilously close to three Natura 2000 sites and cool itself with waters from the nearby Vistula river.
Investment plan for Sostanj lignite power plant TES6 (version 4, unofficial translation)
Official document | 4 August, 2011 | Download PDFThe new version of the investment programme for a new unit at the Sostanj lignite power plant was prepared by the project promoter after the Slovene government expressed doubts over the economic viability of the investment. All the three previous versions of the document were hidden from the public eye.




