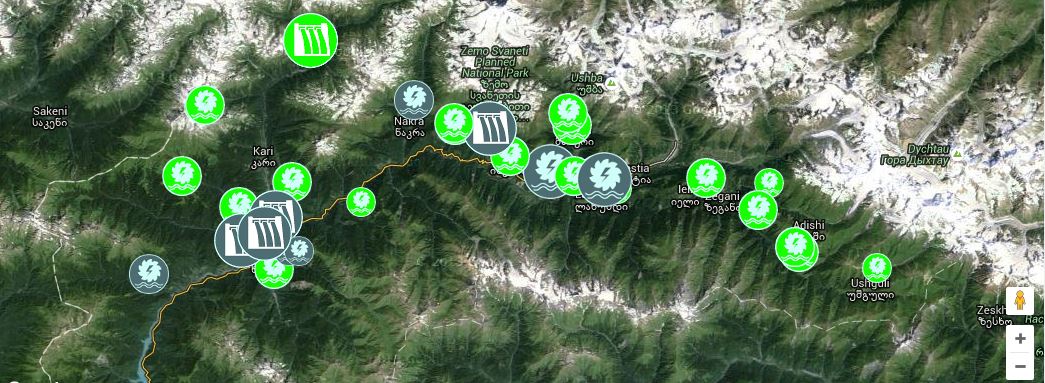
Hydropower development in Georgia
Georgia plans to build a huge number of dams. Yet with 85 percent of electricity needs satisfied and exports not being taxed, these plans will rather benefit private investors than offering sustainable development for Georgia.

Stay informed
We closely follow international public finance and bring critical updates from the ground.
Key issues
- large dams will have adverse impacts on local communities’ livelihoods – more >>
- a cascade of projects will reshape the pristine mountain area of Upper Svaneti – more >>
- land- and mud slides have already resulted in casualties, yet geological risks are not properly assessed – more >>
- legal framework in Georgia offers limited protection for people affected by expropriation and resettlement – more >>
Background
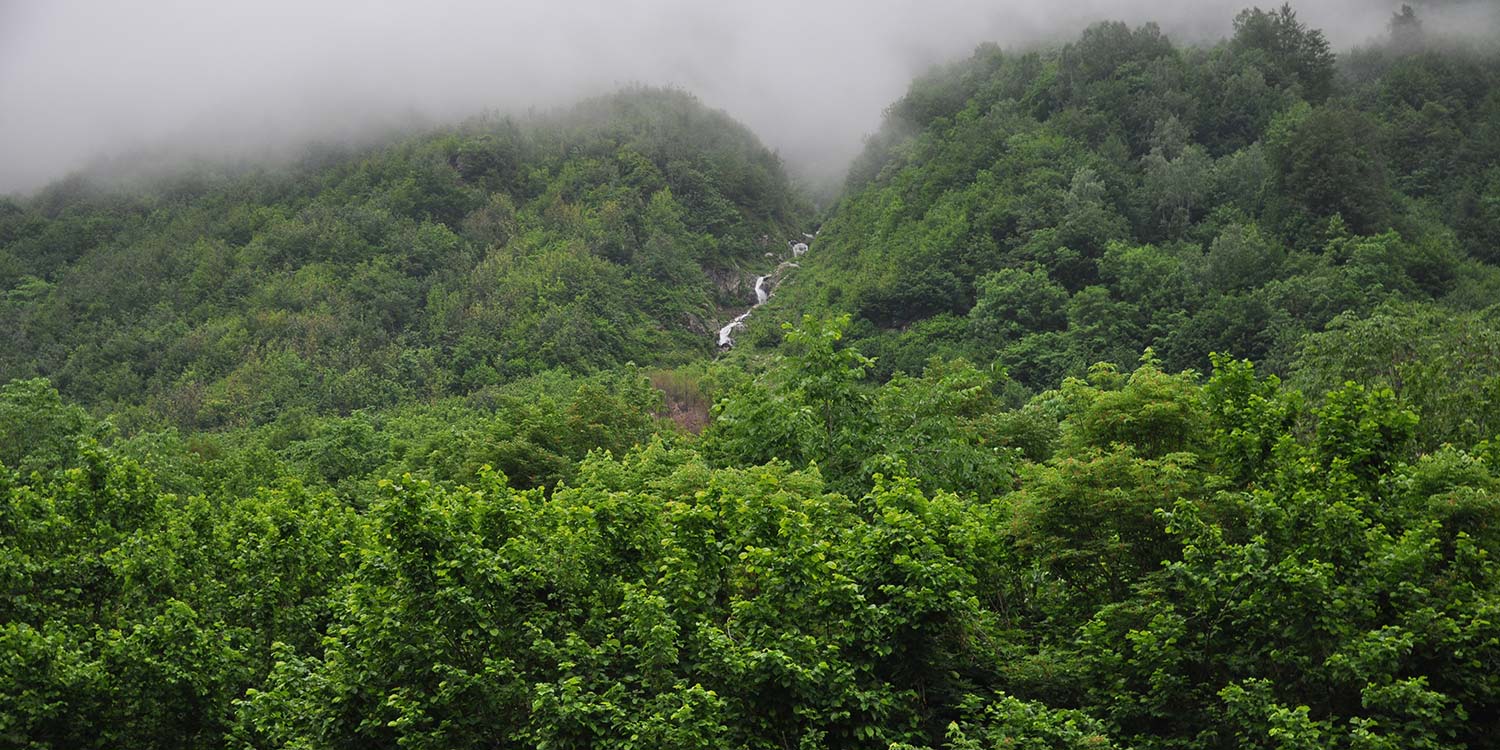
Blessed with staggering mountains, Georgia has a largely unexploited hydropower potential on which private investors, the Georgian government and international lenders have set their sight.
Experience and ongoing monitoring shows that while some hydropower projects would only bring marginal, if any, benefits for locals, the risks associated with them are largely being underestimated or ignored.
Large dams versus local communities
Khudoni
By far the most controversial hydropower project in Georgia is the Khudoni dam. It will interfere with a rich cultural heritage and 2000 people will have to be forcefully resettled.
At the same time the opaque ownership of the project company (registered in a tax haven) and its contractual obligations make the purported benefits of the 702 MW project doubtful.
Nenskra
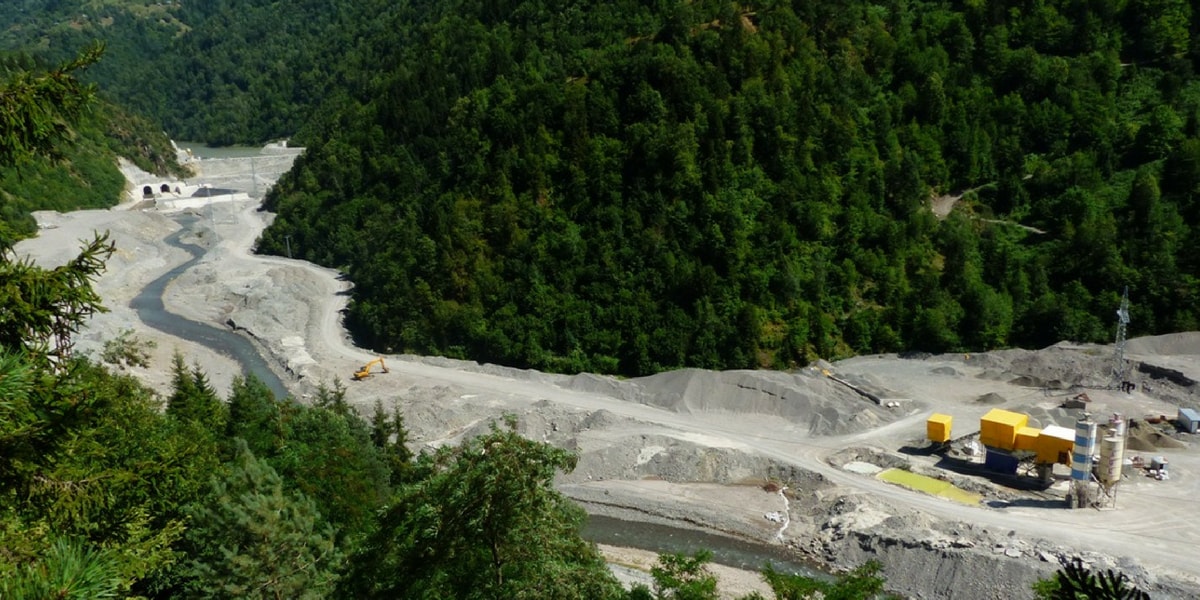
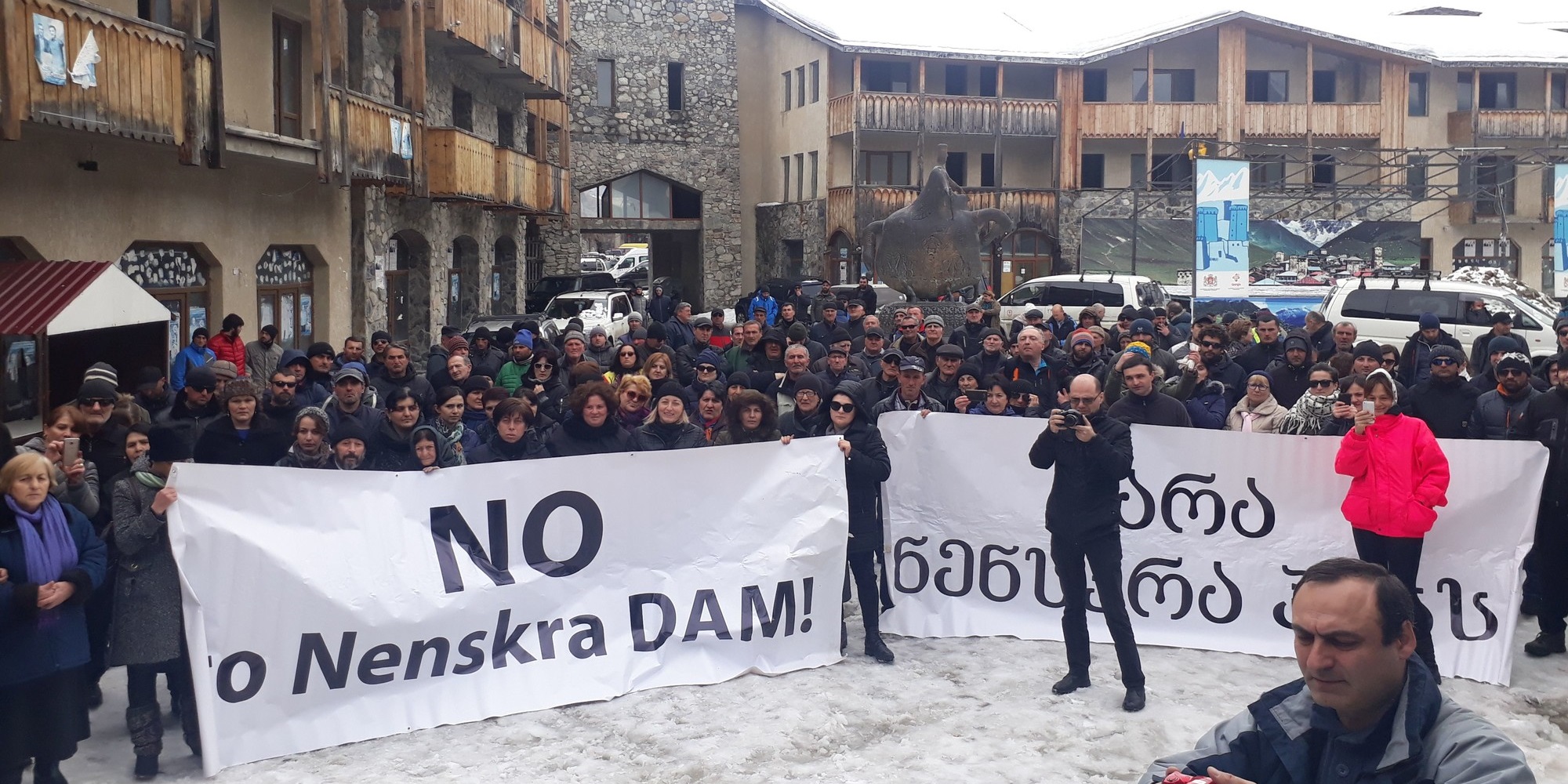
Not far from the site for Khudoni, another controversial large dam project, the 280 MW Nenskra hydropower plant, is being planned. It is the most advanced of Georgia’s massive plans for hydropower installations in the Upper Svaneti region.
It will deprive the local community of ethnic Svans of lands and livelihoods, but potential negative impacts have not been properly assessed.
A historical view on the Georgian energy sector, the effects on local communities and the role of international financial institutions.
Geological hazards in mountain areas
Also smaller projects like the Dariali (pdf) and the Shuakhevi (pdf) HPPs can pose substantial risks, even when no dams have to be built.
Apart from damaging the rivers’ biodiversity, the projects are being constructed without proper assessment of the geological conditions. Two fatal landslides in the Dariali Gorge revealed the irresponsible decision-making by the investors and the Georgian government.
Read more
Second fatal landslide in Georgian Dariali valley
Blog post | August 22, 2014
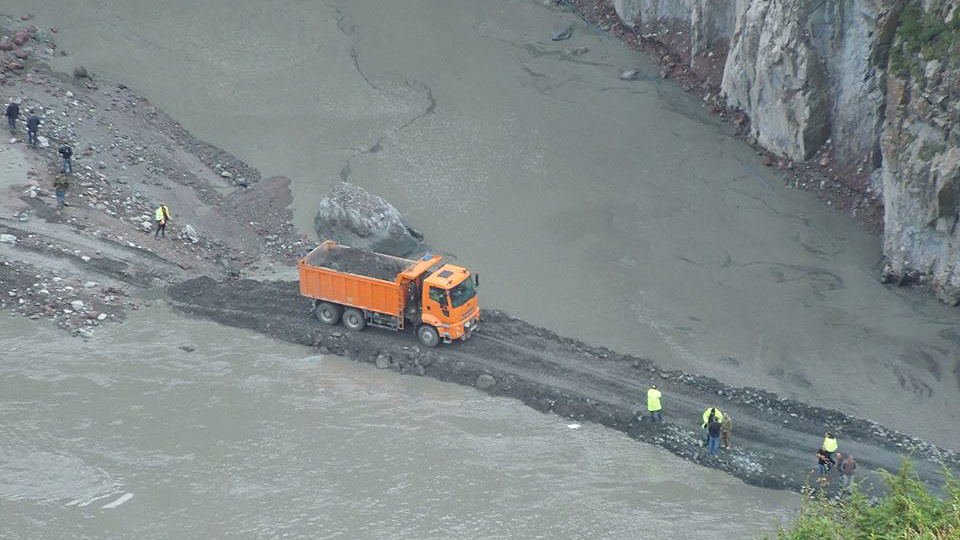

Landslides happened at the site of the Dariali hydropower construction. (Original image by Iago Kazalikashvili.)
Al Jazeera visited Georgia’s hydropower projects to report on constructions in seismically active areas.
Resettlement and lack of legal protection
Georgian communities that face hydropower projects have difficulties protecting their rights as affected stakeholders and landowners.
- Georgia’s legislation does not address the issue of involuntary resettlement caused by infrastructure projects.
- The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) system is ineffective in Georgia, both in terms of providing the public with information and opportunities for public participation (pdf).
- An unclear legal rights regime offers no or minimal protection for communities that make customary use of land that traditionally was in their hands. Unregistered land plots can literally be grabbed by investors for infrastructure projects.
In addition to the threat of losing their land or being resettled, farmers may have to face reduced access to water for irrigation or higher risk of flooding due to dam constructions. Both exposes them to an increased food insecurity.
Related projects
Shuakhevi hydropower plant, Georgia
Georgia’s biggest and one of the most controversial hydropower plants is mostly famous for its failures. Two months after becoming operational in 2017 its tunnels collapsed. And after two years of repairs water is leaking from the dam. Shuakhevi hydropower plant (HPP) once promised to bring energy independence to Georgia. Instead it managed to collect an impressive ‘portfolio’ of problems in a wide range of areas: from biodiversity, to gender impacts, to community relations.
Nenskra hydropower plant, Georgia
The Nenskra dam is the largest of Georgia’s massive plans for hydropower installations in the Upper Svaneti region. If realized, it will deprive the local indigenous communities of their ancestral lands and traditional livelihoods, and cause an irreversible damage to the fragile river and mountain ecosystems.
Khudoni hydropower plant, Georgia
While a mountain community will have to be forced to resettle for this mega-project, the opaque ownership and weak taxation mean that benefits for Georgia are highly doubtful.
Latest news
European Parliament fails to halt disastrous hydropower project jeopardising local livelihoods and endangered species
Press release | 27 September, 2024WWF and CEE Bankwatch Network question the EU Commission’s reasons for putting this decades-old project on the Danube river on its priority investment list.
Read moreActivists say Bosnian dam threatens river life and rafters
Bankwatch in the media | 26 June, 2024KONJIC, Bosnia, June 25 (Reuters) – Environmental activist Lejla Kusturica stood on the banks of Bosnia and Herzegovina’s Neretva river, …
Read moreBattling Rapids and Regulation: Neretva River’s Eco-Warrior Stands Tall
Bankwatch in the media | 25 June, 2024Lejla Kusturica, a Bosnian environmental activist, is concerned about the impact of a new hydro-power dam on the Neretva river’s ecosystem …
Read moreRelated publications
Kungrad 1-3 wind power project, Uzbekistan
Policy comments | 11 March, 2025 | Download PDFKungrad is one of several large-scale renewable projects featuring extensive transmission lines slated for remote, wild areas in Central Asia – an alarming practice that hinders the sustainable energy transition.
How to interact with development banks lending to hydropower projects in Central Asia: A toolkit for civil society activists
Toolkit | 3 February, 2025 | Download PDFThis toolkit is aimed primarily at civil society organisations in Central Asia tackling the construction of dams or other unsustainable water infrastructure.
The Upper Horizons complex, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Briefing | 18 December, 2023 | Download PDFThe Upper Horizons hydropower complex has been planned since the mid-20th century, and is planned to consist of three plants — Dabar, Nevesinje and Bileća — linked by a series of tunnels and channels. If completed, it would have a devastating impact on the karst ecosystems of eastern Herzegovina and beyond.